Was this page helpful?
Caution
You're viewing documentation for a previous version. Switch to the latest stable version.
Integrate Scylla with KairosDB¶
About KairosDB¶
KairosDB is a fast distributed scalable time-series database. It was initially a rewrite of the original OpenTSDB project, but it evolved into a different system where data management, data processing, and visualization are fully separated. When KairosDB introduced native CQL support in version 1.2.0, we created a performance test for KairosDB and Scylla. Through this process, we discovered how easily both platforms could be integrated with each other. The results are presented here in an example that you can adapt to suit your needs. More information on KairosDB can be found on the KairosDB website.
Benefits of integrating KairosDB with Scylla¶
A highly available time-series solution requires an efficient, tailored frontend framework and a backend database with a fast ingestion rate. KairosDB provides a simple and reliable way to ingest and retrieve sensors’ information or metrics, while Scylla provides a highly reliable, performant, and highly available backend that scales indefinitely and can store large quantities of time-series data.
Use case for integration¶
The diagram below shows a typical integration scenario where several sensors (in this case, GPU temperature sensors) are sending data to KairosDB node(s). The KairosDB nodes are using a Scylla cluster as a backend datastore. To interact with KairosDB, there is a web based UI.
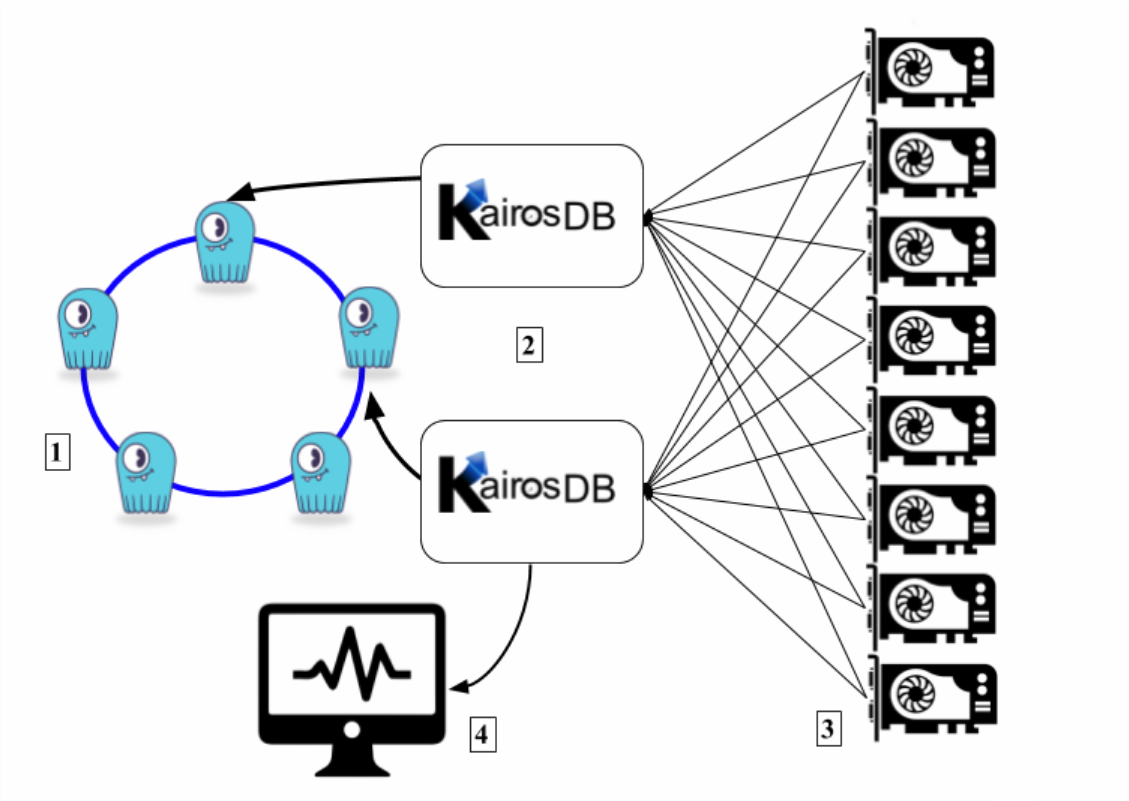
Legend
Scylla cluster
KairosDB nodes
GPU sensors
WebUI for KairosDB
Integration example¶
Recommendations¶
In order to implement this integration example, the following are recommendations:
It is recommended to deploy KairosDB separately from Scylla, to prevent the databases from competing for resources.
Make sure to have sufficient disk space, as KairosDB accumulates data files queued on disk.
KairosDB requires Java (and JAVA_HOME setting) as per the procedure here.
Resource list¶
Although your requirements may be different, this example uses the following resources:
Scylla cluster: 3 x i3.8XL instances
KairosDB node: m5.2XL instance(s)
Loaders (python script emulating the sensors): m5.2XL instance(s)
Disk space 200GB for the KairosDB nodes
Note that in this case, 200GB was sufficient, but your disk space depends on the workload size from the application/s into Kairos and the speed in which KairosDB can handle the load and write it to the Scylla backend datastore.
Integration instructions¶
The commands shown in this procedure may require root user or sudo.
Before you begin
Verify that you have installed Scylla on a different instance/server and that you know the Scylla server IP address.
Procedure
Download KairosDB. This example downloads version 1.2.0.
sudo curl -O --location https://github.com/kairosdb/kairosdb/releases/download/v1.2.0/kairosdb-1.2.0-1.tar.gz
Extract KairosDB.
sudo tar xvzf kairosdb-1.2.0-1.tar.gz
Configure KairosDB to connect to the Scylla server. Using an editor, open the
kairosdb/conf/kairosdb.propertiesfile and make the following edits:Comment out the H2 module
#kairosdb.service.datastore=org.kairosdb.datastore.h2.H2Module
Uncomment the Cassandra module
kairosdb.service.datastore=org.kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.CassandraModule
In the
#Cassandra propertiessection, set the Scylla nodes IPkairosdb.datastore.cassandra.cql_host_list=[IP1],[IP2]...
Set the replication factor (for production purposes use a Scylla cluster with a minimum of RF=3)
kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.replication={'class': 'NetworkTopologyStrategy','replication_factor' : 3}Set the read and write consistency level (for production purposes use write=ONE, read=QUORUM)
kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.read_consistency_level=QUORUM kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.write_consistency_level=ONE (sufficient for time series workload)
In case your Scylla / Cassandra cluster is deployed on multiple data centers, change the local datacenter parameter to match the data center you are using.
kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.local_datacenter=[your_local_DC_name]
Set connections per host to match the # of shards that Scylla utilizes. Check the number of shards by running the following command on your scylla nodes:
> cat /etc/scylla.d/cpuset.conf CPUSET="--cpuset 1-15,17-31"
In this case, Scylla is using 30 CPU threads (out of 32) as 1 physical core is dedicated to interrupts handling. Set the following Kairos connections:
kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.connections_per_host.local.core=30 kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.connections_per_host.local.max=30 kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.connections_per_host.remote.core=30 kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.connections_per_host.remote.max=30
Set max requests per connection to a smaller value than the default (default = 128). As the client only moves to a new connection after it saturates the first. Setting it to a smaller value will cause it to move to a new connection sooner:
kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.max_requests_per_connection.local=8 kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.max_requests_per_connection.remote=8
Set the Kairos batch size (default = 200) and the minimum batch size (default = 100). Testing found that it is necessary to use a smaller value than the default setting. This was because one of Scylla’s shard handling batches can spike to 100% CPU when handling a heavy load from Kairos, which leads to write timeout and poor latency results. In the example, we found the best performance when it is set to 50. When we deployed three Kairos nodes, we divided the load so that each node was set to 15.
kairosdb.queue_processor.batch_size=50 kairosdb.queue_processor.min_batch_size=50
Set the ingest executor thread count (default = 10). In our example, we found 20 to yield the best results.
kairosdb.ingest_executor.thread_count=20
Optional: enable TTL for data points. Set the Time to Live value. Once the threshold is reached, the data is deleted automatically. If not set, the data is not deleted. TTLs are added to columns as they’re inserted. Note that setting the TTL does not affect existing data, only new data. Additional TTL parameters to use at your discretion (see their explanation in the properties file)
#kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.datapoint_ttl=31536000 (Time to live in seconds for data points)
kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.align_datapoint_ttl_with_timestamp=false
kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.force_default_datapoint_ttl=false
Using multiple Kairos instances (optional). You might need to use more than a single KairosDB instance to push more data into Scylla, as there are some limits in the Cassandra client that prevents a single kairos instance from pushing faster. To deploy multiple Kairos nodes, shard the clients / sensors, and assign several ingesting clients per Kairos node. Note that in this case, the data is not divided, but each Kairos node is assigned to several clients.
Start KairosDB process. Change to the bin directory and start KairosDB using one of the following commands:
To start KairosDB and run it in the foreground:
> sudo ./kairosdb.sh run
To run KairosDB as a background process:
> sudo ./kairosdb.sh start
To stop KairosDB when running as a background process:
> sudo ./kairosdb.sh stop
To verify that the KairosDB Schema was created properly in your Scylla cluster, connect to one of the Scylla cluster nodes and open cql shell:
> cqlsh [node IP]
Check that the keyspace and tables were created (default keyspace = kairosdb):
cqlsh> DESC TABLES
Keyspace kairosdb
----------------
row_keys data_points string_index
row_key_index service_index row_key_time_index
Check that the ‘kairosdb’ schema exists and verify the keyspace replication factor:
cqlsh> DESC KEYSPACE kairosdb
Ansible playbook¶
A KairosDB deployment Ansible playbook for your use is available on github. It requires that you install Ansible v2.3 or higher and that a Scylla cluster up and running.
Setup Ansible playbook¶
Procedure
Set the following variables in kairosdb_deploy.yml file:
Scylla node(s) IP address(es)
Number of shards per node that Scylla utilizes (cat /etc/scylla.d/cpuset.conf)
KairosDB batch size - when using a single KairosDB instance with Scylla, while Scylla runs on i3.8XL instance, the value should be set to ‘50’. When using multiple KairosDB nodes, or when Scylla runs on smaller instances, the value should be lower. If you are using multiple KairosDB nodes, you need to divide the batch size evenly per node.
Run the playbook:
Run locally: add
‘localhost ansible_connection=local’to the/etc/ansible/hostsfileRun on remote nodes: add an entry for each node’s IP in the
/etc/ansible/hostsfileIf you want to enable key checking, in the ansible-playbook kairosdb_deploy.yml file change the
ANSIBLE_HOST_KEY_CHECKING=Falseto true.
